Physician Net Worth by Age: A Comprehensive Look at Financial Health
Let's talk frankly about physician finances. While many physicians enjoy high incomes, the reality is that net worth varies dramatically, even among doctors in the same specialty and age group. Understanding the factors influencing this disparity is crucial for building a secure financial future. Some physicians are accumulating substantial wealth, while others struggle. This article aims to demystify this variance and provide actionable steps for improving your own financial trajectory. For high-net-worth divorce concerns, see this resource.
Are you building wealth at the pace you desire? The following sections delve into factors impacting physician net worth, offering practical strategies for financial success at every career stage.
Decoding Physician Net Worth: Key Factors at Play
While a significant portion of physicians (50-60%) report a net worth of at least $1 million, a considerable minority (20-40%) have less than half that amount. This isn’t simply a matter of chance; several key factors shape financial outcomes.
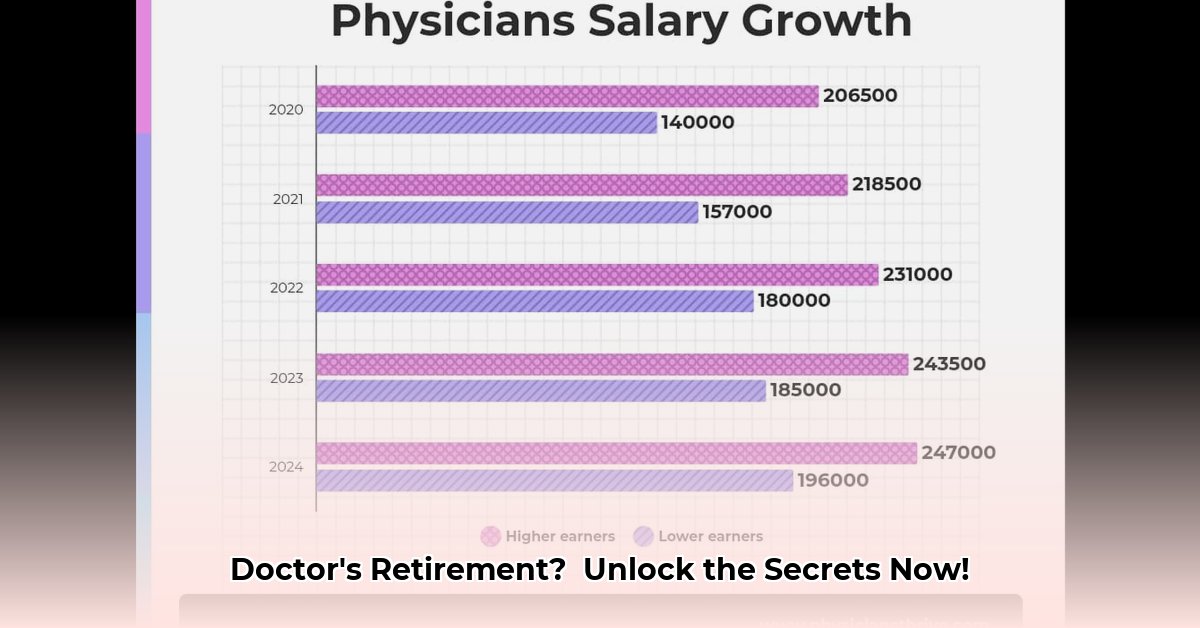
Specialty and Income: A Significant Driver
Different medical specialties command vastly different salaries. High-earning specialties like cardiology and neurosurgery typically offer substantially higher incomes than family medicine, directly impacting wealth accumulation. Choosing a specialty requires careful consideration of both career fulfillment and long-term financial implications. Exploring options that balance both areas is often wise.
Gender and Wealth: Addressing the Disparity
Studies consistently highlight a wealth gap between male and female physicians. While the reasons are complex and multifaceted, potential factors include societal expectations, career interruptions for family responsibilities, and potential pay disparities. Further research is needed to fully understand and address this persistent gap.
Financial Literacy: Knowledge is Power
Even high earners can struggle financially without strong financial literacy. Understanding investing, retirement planning, and debt management isn't optional; it's fundamental for building wealth. Lack of financial know-how can impede wealth accumulation regardless of income level.
Managing Debt: A Crucial Element of Wealth Building
Many physicians graduate with substantial student loan debt, significantly impacting early-career wealth building. While medical school debt is a near-universal experience, proactive debt management strategies are critical for accelerating wealth accumulation. Mortgages, car loans and other debts further impact financial progress.
Building Your Physician Wealth: Actionable Steps
Wealth building is a long-term endeavor, not a sprint. Consistent, strategic decision-making is key.
Seek Professional Financial Advice: A financial advisor can tailor a plan to your specific needs, offering personalized guidance on investing, retirement planning, and tax optimization.
Strategically Manage Debt: Aggressively pay off high-interest debt. Explore options like debt consolidation to free up funds for investment and growth.
Automate Your Savings: Set up automatic transfers to savings and investment accounts. Treat saving as a non-negotiable expense. Compound interest is a powerful tool over time.
Diversify Your Investments: Spread investments across different asset classes (stocks, bonds, real estate) to mitigate risk. This strategy is crucial in volatile markets, safeguarding against potentially significant losses.
Embrace Continuous Learning: Stay updated on financial best practices, investment strategies, and tax laws through courses, workshops, or reputable financial publications.
Securing Your Retirement: A Long-Term Strategy
Retirement planning is an ongoing process, not a one-time event. Regular review and adjustment of your financial plan, especially as circumstances or expertise evolves, are essential.
Mitigating Financial Risks: A Proactive Approach
The following table showcases potential risks and mitigation strategies:
| Risk Factor | Likelihood | Impact | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Under-saving for retirement | High | High | Maximize retirement contributions; consider a Roth IRA; disciplined budgeting |
| High levels of physician debt | Medium | Medium | Aggressive debt repayment; explore loan refinancing options; financial counseling |
| Market volatility | Medium | Medium | Diversified investment portfolio; long-term investment horizon; professional financial advice |
| Unexpected career interruptions | Low | High | Disability insurance; emergency fund; explore alternative income streams |
| Lack of financial literacy | High | High | Financial education courses; work with a financial planner |
Key Takeaways for Physician Financial Success
- Effective financial planning requires understanding spending habits for accurate retirement projections.
- Account for a long lifespan when planning retirement. The 4% rule is a guideline, not a guarantee of success. Consider your risk tolerance carefully.
- Long-term investment strategies using diversified portfolios are vital for successful wealth accumulation.
- High-income earners like physicians require substantial retirement savings. Social Security provides support, but shouldn't be the sole reliance.
Your financial journey is personal. By proactively managing risks, engaging in strategic planning, and seeking expert guidance, you can build a secure financial future.